Strapi-v4
What is Multitenancy?
Multitenancy refers to a kind of architecture where a single instance of software runs on a server and serves multiple customers. In a multi-tenant environment, separate customers tap into the same hardware and data storage, creating a dedicated instance for each customer. Each tenant’s data is isolated and remains invisible to others, but is running on the same server.
Introduction
In this guide, we will create an application with you in the logic of Multi Tenant(Multitenancy). We can say multi tenant application is separate and manage multiple contents independently from each other in a single application.
We will make a Cake House application using refine and Strapi-v4. Our Cake House will consist of two separate stores and there will be special products for these stores. We will explain step by step how to manage these stores, products, and orders separately.
This guide has been prepared to assume you know the basics of refine. If you haven't learned these basics yet, we recommend reading the Tutorial.
Setup
npm i @pankod/refine-strapi-v4
To make this example more visual, we used the @pankod/refine-antd package. If you are using Refine headless, you need to provide the components, hooks, or helpers imported from the @pankod/refine-antd package.
Usage
AuthProvider
Show Code
import { AuthProvider } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import { AuthHelper } from "@pankod/refine-strapi-v4";
import axios from "axios";
export const axiosInstance = axios.create();
const API_URL = "YOUR_API_URL";
const TOKEN_KEY = "strapi-jwt-token";
const strapiAuthHelper = AuthHelper(API_URL + "/api");
export const authProvider: AuthProvider = {
login: async ({ username, password }) => {
const { data, status } = await strapiAuthHelper.login(
username,
password,
);
if (status === 200) {
localStorage.setItem(TOKEN_KEY, data.jwt);
// set header axios instance
axiosInstance.defaults.headers.common["Authorization"] = `Bearer ${data.jwt}`;
return Promise.resolve();
}
return Promise.reject();
},
logout: () => {
localStorage.removeItem(TOKEN_KEY);
return Promise.resolve();
},
checkError: () => Promise.resolve(),
checkAuth: () => {
const token = localStorage.getItem(TOKEN_KEY);
if (token) {
axiosInstance.defaults.headers.common["Authorization"] = `Bearer ${token}`,
return Promise.resolve();
}
return Promise.reject();
},
getPermissions: () => Promise.resolve(),
getUserIdentity: async () => {
const token = localStorage.getItem(TOKEN_KEY);
if (!token) {
return Promise.reject();
}
const { data, status } = await strapiAuthHelper.me(token);
if (status === 200) {
const { id, username, email } = data;
return Promise.resolve({
id,
username,
email,
});
}
return Promise.reject();
},
};
If you need the population for the /me request, you can use it like this in your authProvider.
const strapiAuthHelper = AuthHelper(API_URL + "/api");
strapiAuthHelper.me("token", {
metaData: {
populate: ["role"],
},
});
import { Refine } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import {
Layout,
ReadyPage,
notificationProvider,
ErrorComponent,
} from "@pankod/refine-antd";
import { DataProvider } from "@pankod/refine-strapi-v4";
import routerProvider from "@pankod/refine-react-router-v6";
import "@pankod/refine-antd/dist/reset.css";
import { authProvider, axiosInstance } from "./authProvider";
const API_URL = "YOUR_API_URL";
const App: React.FC = () => {
return (
<Refine
authProvider={authProvider}
dataProvider={DataProvider(API_URL + "/api", axiosInstance)}
routerProvider={routerProvider}
Layout={Layout}
ReadyPage={ReadyPage}
notificationProvider={notificationProvider}
catchAll={<ErrorComponent />}
/>
);
};
You can find detailed usage information and the source code here.
Create Collections
We created three collections on Strapi as store, product, and order and added a relation between them. For detailed information on how to create a collection, you can check here.
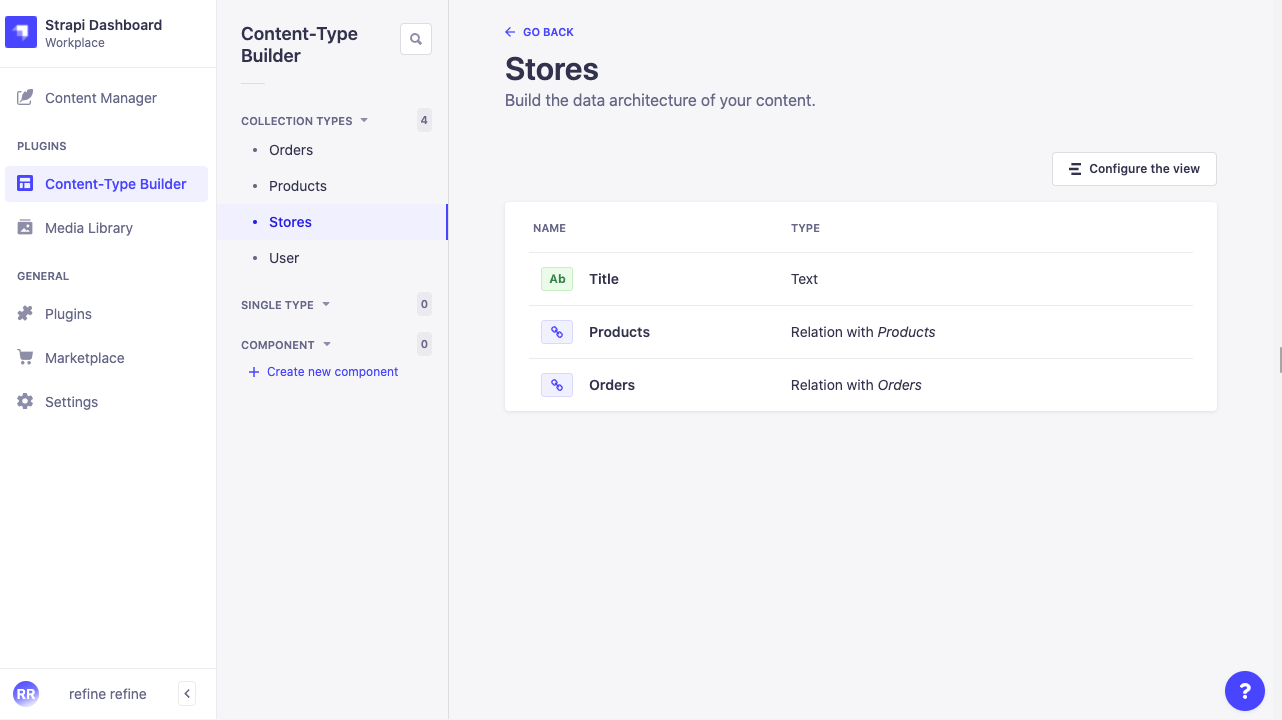
Stores
- Title: Text
- Relation with Products
- Relation with Orders
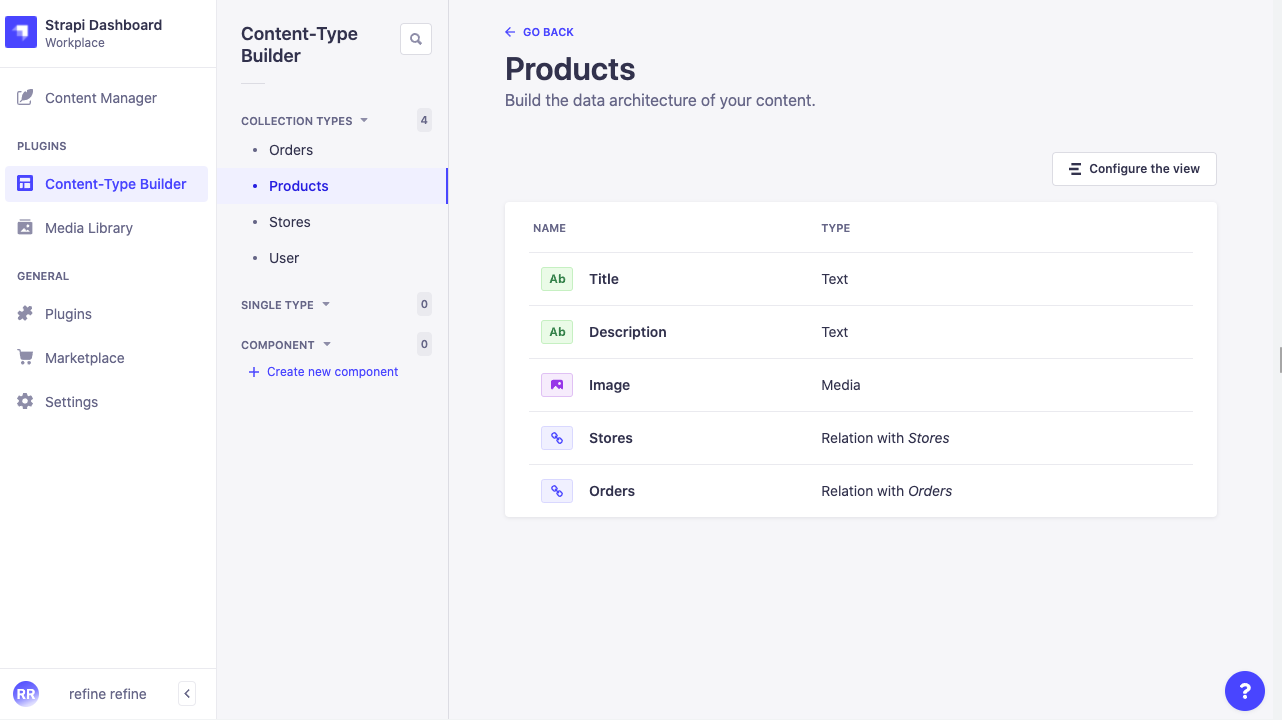
Products
- Title: Text
- Description: Text
- Image: Media
- Relation with Stores
- Relation with Orders
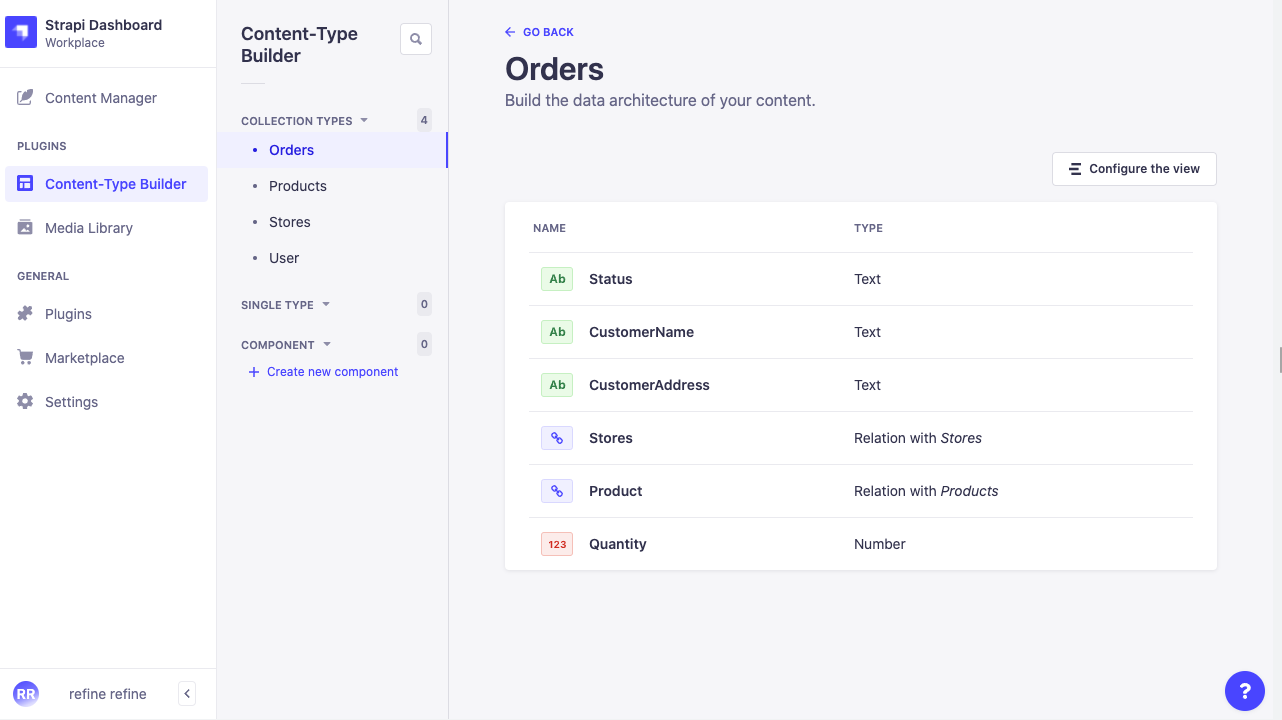
Orders
- Status: Text
- Customer Name: Text
- Customer Address: Text
- Quantity: Number
- Relation with Stores
- Relation with Product
Now that we have completed the setup and our collections, we can now log in with the refine and start the listing processes.
Store Context
To view the products and orders of two different stores separately, we need to filter by storeId. We will use the storeId information in more than one place. For example, when creating a store-specific order.
For this reason, we will create a React Context and keep the storeId state information in it and send it to the relevant refine components.
import { createContext, useState } from "react";
export const StoreContext = createContext<any[]>([]);
export const StoreProvider = (props: any) => {
const [store, setStore] = useState(1);
return <StoreContext.Provider value={[store, setStore]} {...props} />;
};
import { Refine } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import {
Layout,
ReadyPage,
notificationProvider,
ErrorComponent,
} from "@pankod/refine-antd";
import { DataProvider } from "@pankod/refine-strapi-v4";
import routerProvider from "@pankod/refine-react-router-v6";
import "@pankod/refine-antd/dist/reset.css";
import { StoreProvider } from "context/store";
import { authProvider, axiosInstance } from "./authProvider";
const API_URL = "YOUR_API_URL";
const App: React.FC = () => {
return (
<StoreProvider>
<Refine
authProvider={authProvider}
dataProvider={DataProvider(API_URL + "/api", axiosInstance)}
routerProvider={routerProvider}
Layout={Layout}
ReadyPage={ReadyPage}
notificationProvider={notificationProvider}
catchAll={<ErrorComponent />}
/>
</StoreProvider>
);
};
Shop Select to Sider Component
We will create a select component in the Sider Menu where the user will select the stores. Let's create our select component first, then let's see how we can define it in the refine Sider.
import { useContext } from "react";
import { Select, useSelect } from "@pankod/refine-antd";
import { StoreContext } from "context/store";
import { IStore } from "interfaces";
type SelectProps = {
onSelect: () => void;
};
export const StoreSelect: React.FC<SelectProps> = ({ onSelect }) => {
const [store, setStore] = useContext(StoreContext);
const { selectProps: storeSelectProps } = useSelect<IStore>({
resource: "stores",
optionLabel: "title",
optionValue: "id",
});
const handleChange = (selectedValue: string) => {
setStore(selectedValue);
};
return (
<Select
defaultValue={store}
style={{ width: 130 }}
onChange={handleChange}
onSelect={onSelect}
>
{storeSelectProps.options?.map(({ value, label }) => (
<Select.Option key={value} value={value}>
{label}
</Select.Option>
))}
</Select>
);
};
Here we have created a select component. Then we fetch the store id and title we created in the Strapi database with useSelect. Now we can place the store information we have in the state we created in the Store Context.
Let's define the select component in the refine Sider Menu. First, we need to customize the default Sider.
Check out how you can customize Sider Menu →
Show Code
import React, { useState } from "react";
import {
useTitle,
useMenu,
useLogout,
CanAccess,
ITreeMenu,
useRouterContext,
} from "@pankod/refine-core";
import { AntdLayout, Menu, Grid, Icons } from "@pankod/refine-antd";
import { StoreSelect } from "components/select";
import { antLayoutSider, antLayoutSiderMobile } from "./styles";
export const CustomSider: React.FC = () => {
const [collapsed, setCollapsed] = useState<boolean>(false);
const { mutate: logout } = useLogout();
const { Link } = useRouterContext();
const Title = useTitle();
const { menuItems, selectedKey } = useMenu();
const breakpoint = Grid.useBreakpoint();
const isMobile =
typeof breakpoint.lg === "undefined" ? false : !breakpoint.lg;
const renderTreeView = (tree: ITreeMenu[], selectedKey: string) => {
return tree.map((item: ITreeMenu) => {
const { icon, label, route, name, children, parentName } = item;
if (children.length > 0) {
return (
<SubMenu
key={route}
icon={icon ?? <Icons.UnorderedListOutlined />}
title={label}
>
{renderTreeView(children, selectedKey)}
</SubMenu>
);
}
const isSelected = route === selectedKey;
const isRoute = !(
parentName !== undefined && children.length === 0
);
return (
<CanAccess
key={route}
resource={name.toLowerCase()}
action="list"
>
<Menu.Item
key={route}
style={{
fontWeight: isSelected ? "bold" : "normal",
}}
icon={
icon ?? (isRoute && <Icons.UnorderedListOutlined />)
}
>
<Link to={route}>{label}</Link>
{!collapsed && isSelected && (
<div className="ant-menu-tree-arrow" />
)}
</Menu.Item>
</CanAccess>
);
});
};
return (
<AntdLayout.Sider
collapsible
collapsedWidth={isMobile ? 0 : 80}
collapsed={collapsed}
breakpoint="lg"
onCollapse={(collapsed: boolean): void => setCollapsed(collapsed)}
style={isMobile ? antLayoutSiderMobile : antLayoutSider}
>
{Title && <Title collapsed={collapsed} />}
<Menu
selectedKeys={[selectedKey]}
mode="inline"
onClick={() => {
if (!breakpoint.lg) {
setCollapsed(true);
}
}}
>
<Menu.Item key={route} icon={<Icons.AppstoreAddOutlined />}>
<StoreSelect
onSelect={() => {
setCollapsed(true);
}}
/>
</Menu.Item>
{renderTreeView(menuItems, selectedKey)}
<Menu.Item
key="logout"
onClick={() => logout()}
icon={<Icons.LoginOutlined />}
>
Logout
</Menu.Item>
</Menu>
</AntdLayout.Sider>
);
};
 |
|---|
As you can see, you can now choose the store you want and create products and orders specifically for the store we have chosen according to the storeId information. |
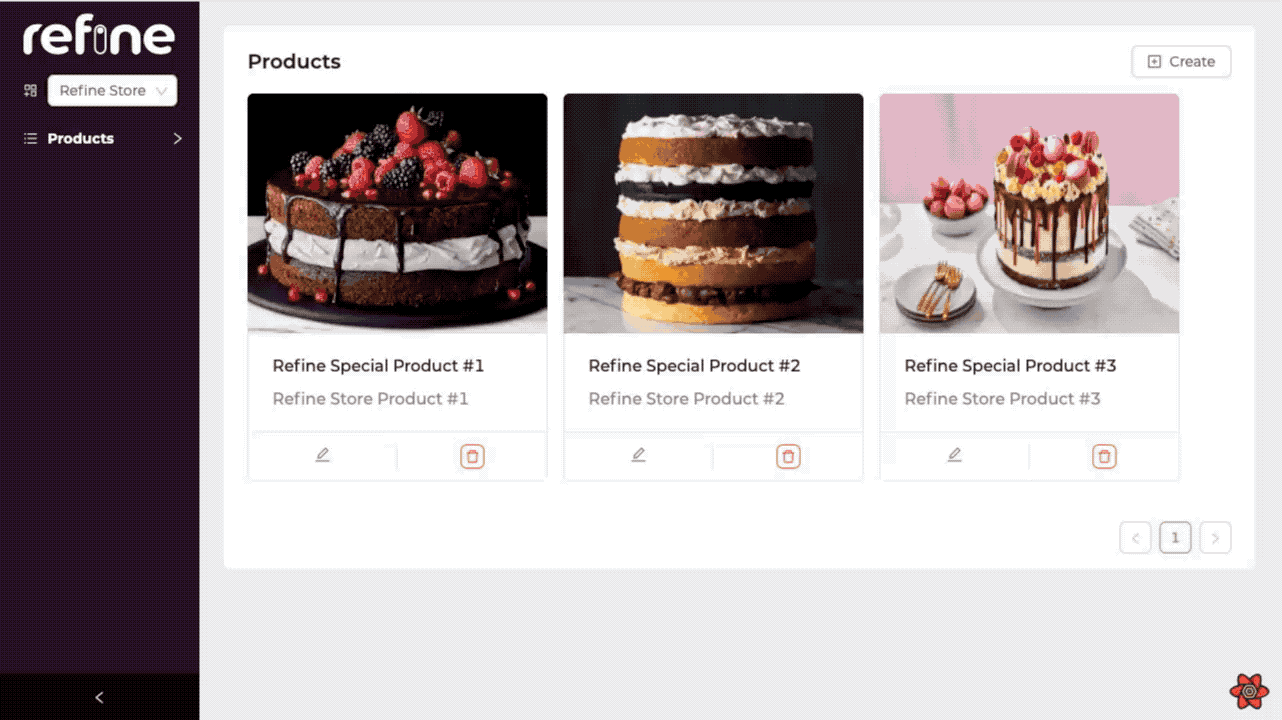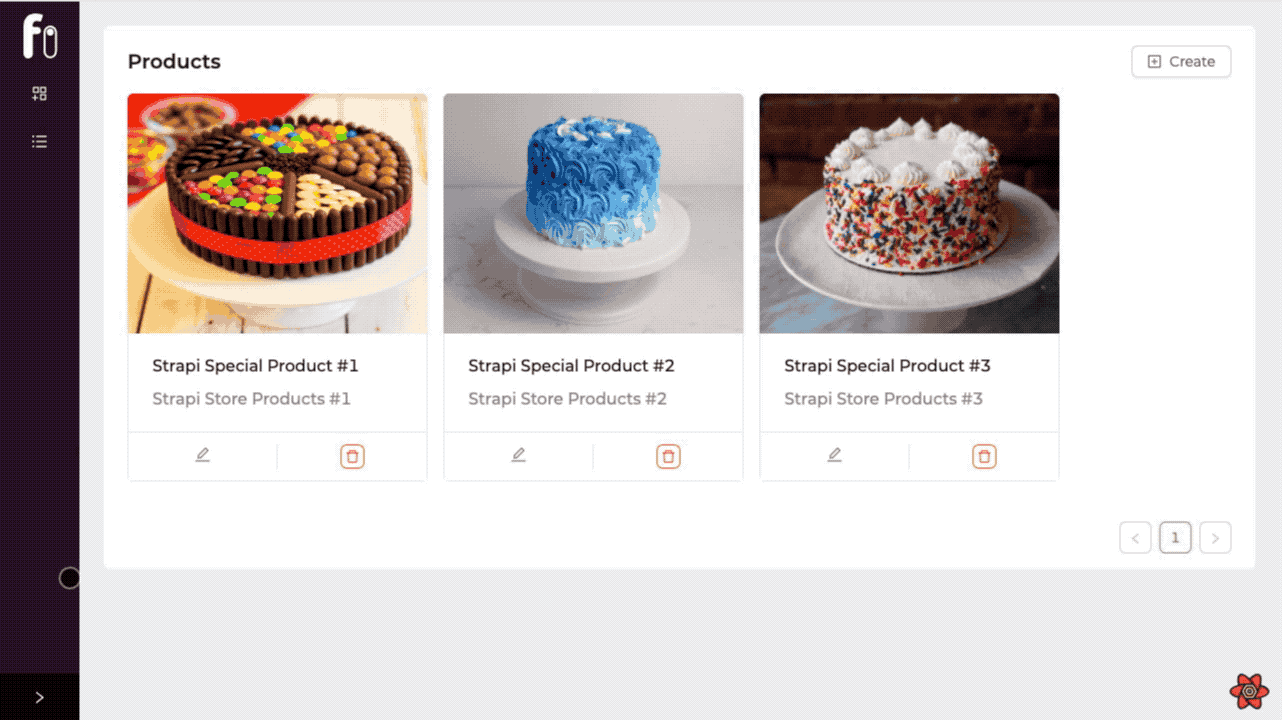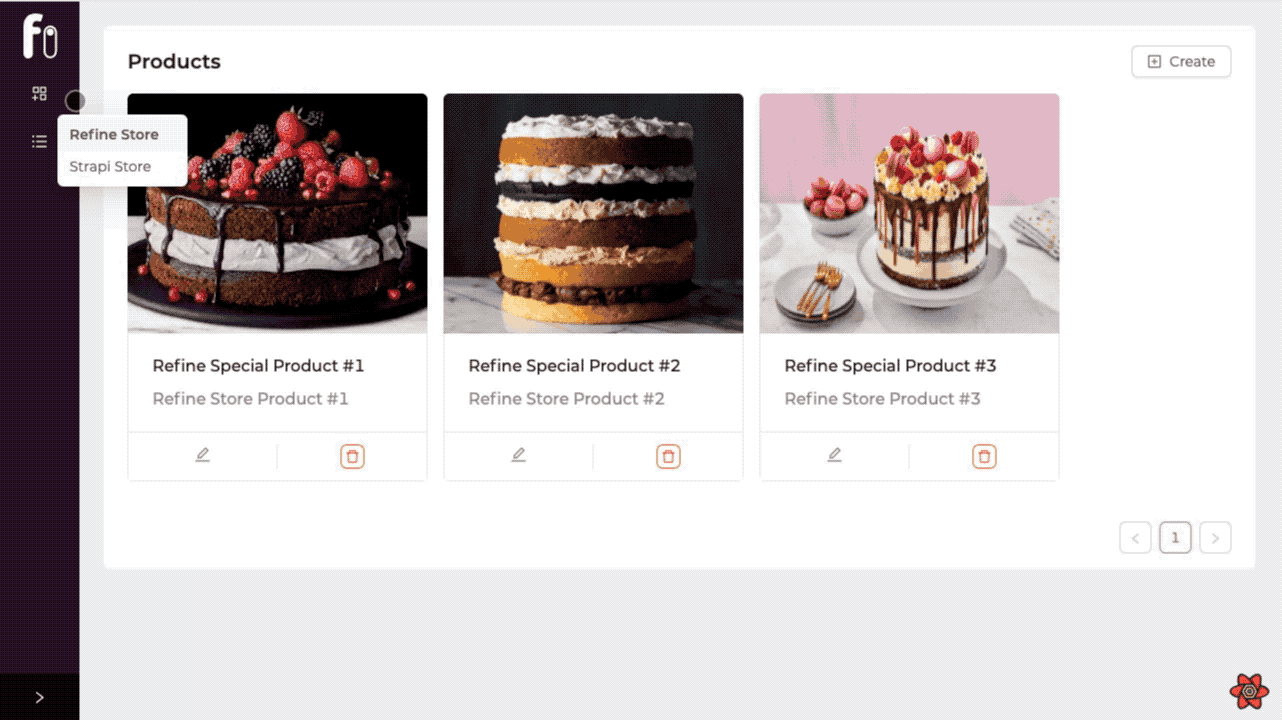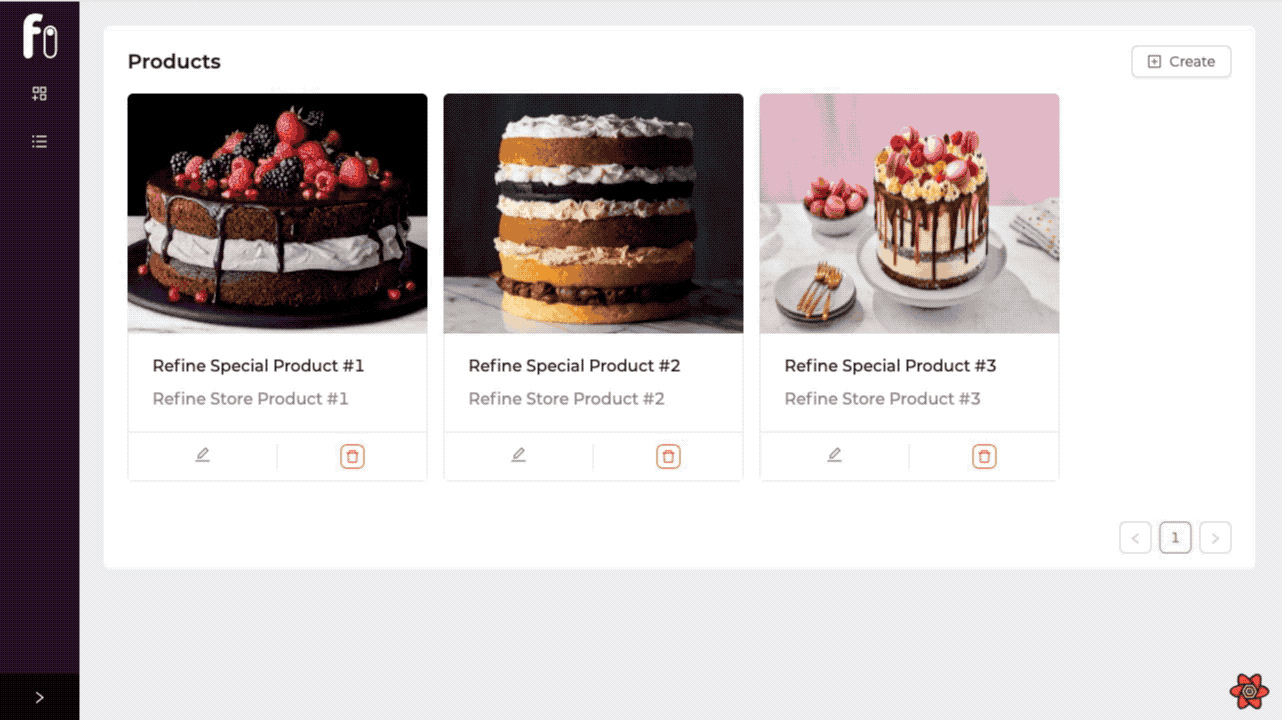
Product List Page
Now we can list the products of the selected store according to the storeId information by filtering it. We can do this filtering by using the permanetFilter property within the refine's useSimpleList hook.
We separate the products of different stores by using the permanentFilter with the storeId we get from the Store Context. So we can control more than single content in one application.
const [store] = useContext(StoreContext);
const { listProps } = useSimpleList<IProduct>({
permanentFilter: [{ field: "stores][id]", operator: "eq", value: store }],
});
Show Code
import { useContext } from "react";
import { IResourceComponentsProps, HttpError } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import {
useSimpleList,
AntdList,
useModalForm,
useDrawerForm,
CreateButton,
List,
} from "@pankod/refine-antd";
import { IProduct } from "interfaces";
import { ProductItem } from "components/product";
import { StoreContext } from "context/store";
export const ProductList: React.FC<IResourceComponentsProps> = () => {
const [store] = useContext(StoreContext);
const { listProps } = useSimpleList<IProduct>({
permanentFilter: [
{ field: "stores][id]", operator: "eq", value: store },
],
metaData: { populate: ["image"] },
});
return (
<List
headerProps={{
extra: <CreateButton onClick={() => createShow()} />,
}}
>
<AntdList
grid={{ gutter: 16, xs: 1 }}
style={{
justifyContent: "center",
}}
{...listProps}
renderItem={(item) => (
<AntdList.Item>
<ProductItem item={item} editShow={editShow} />
</AntdList.Item>
)}
/>
</List>
);
};
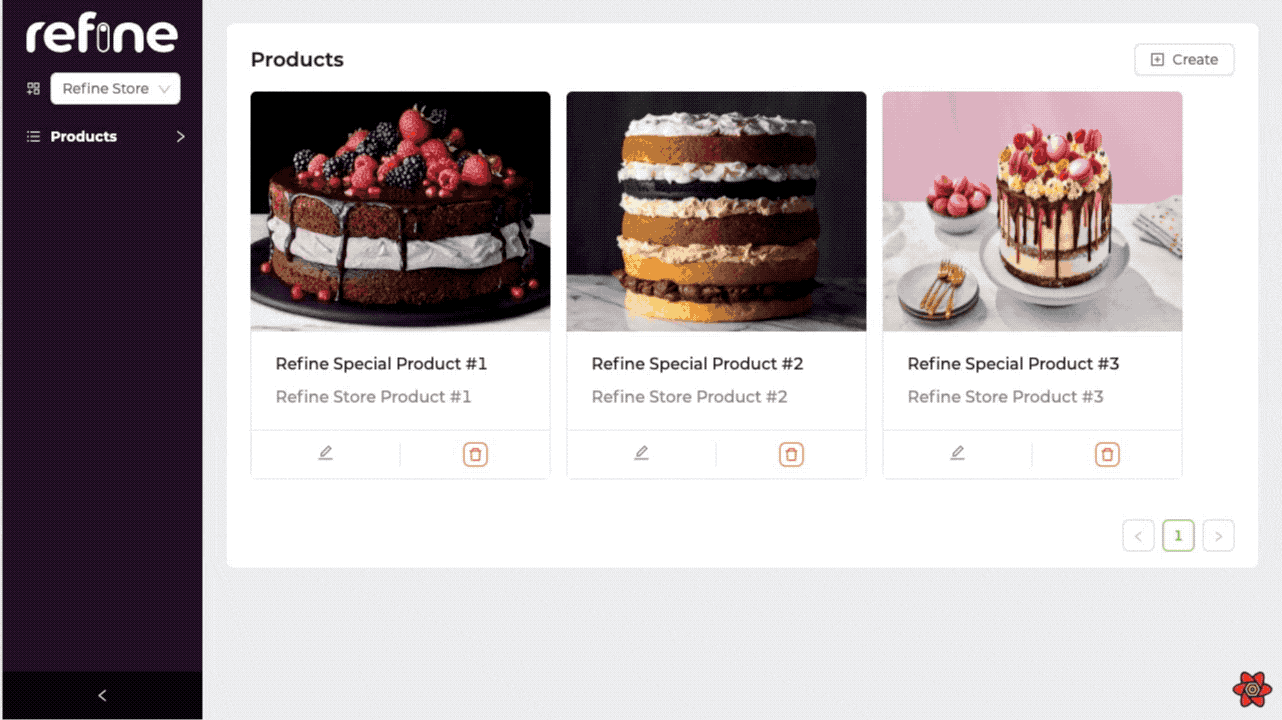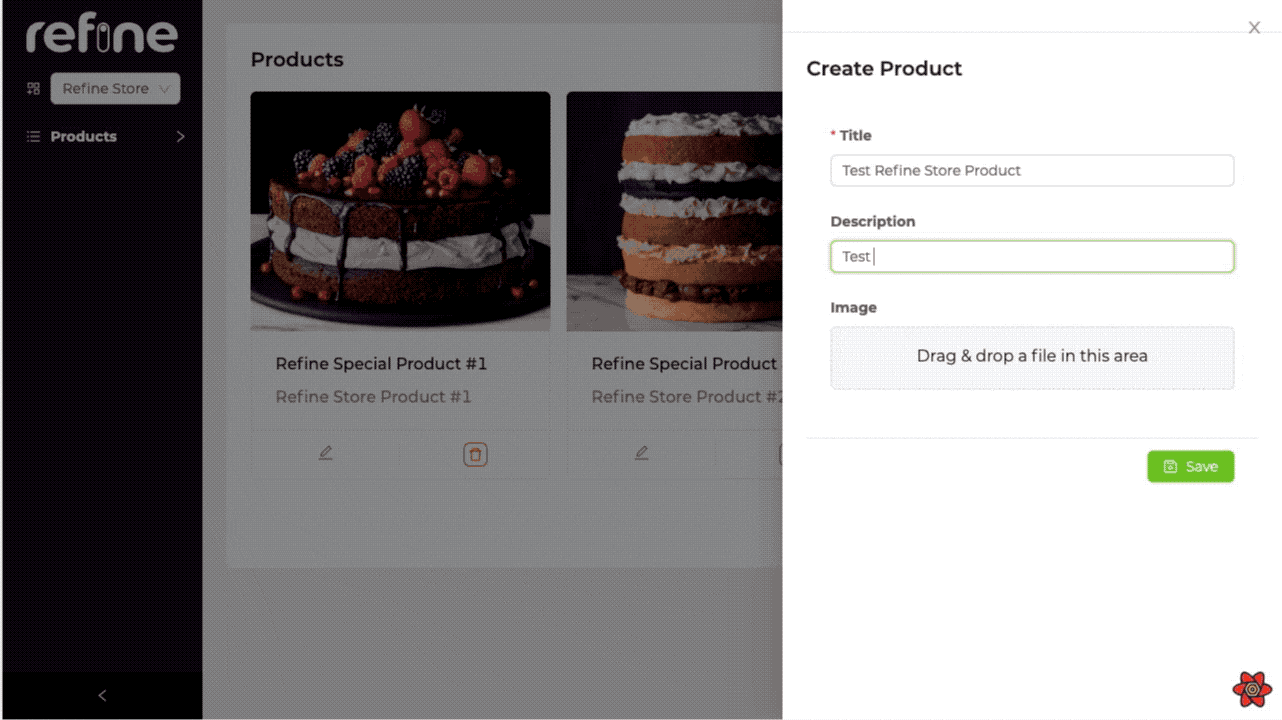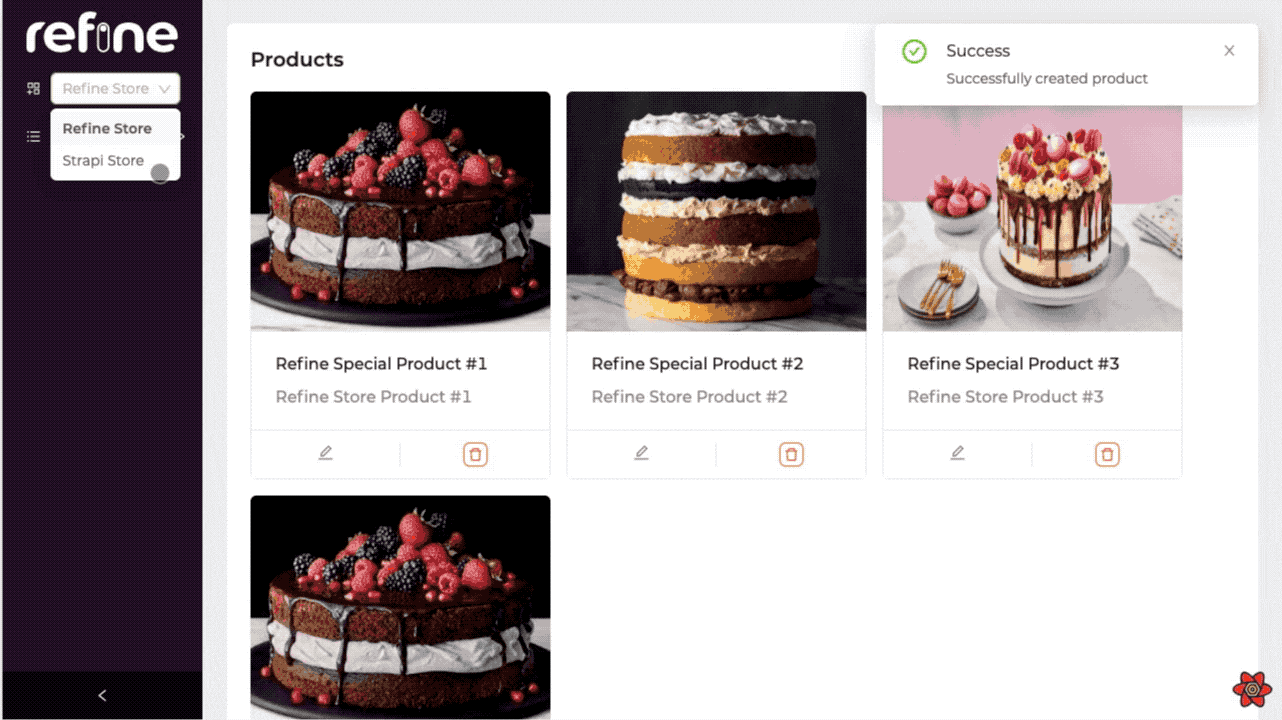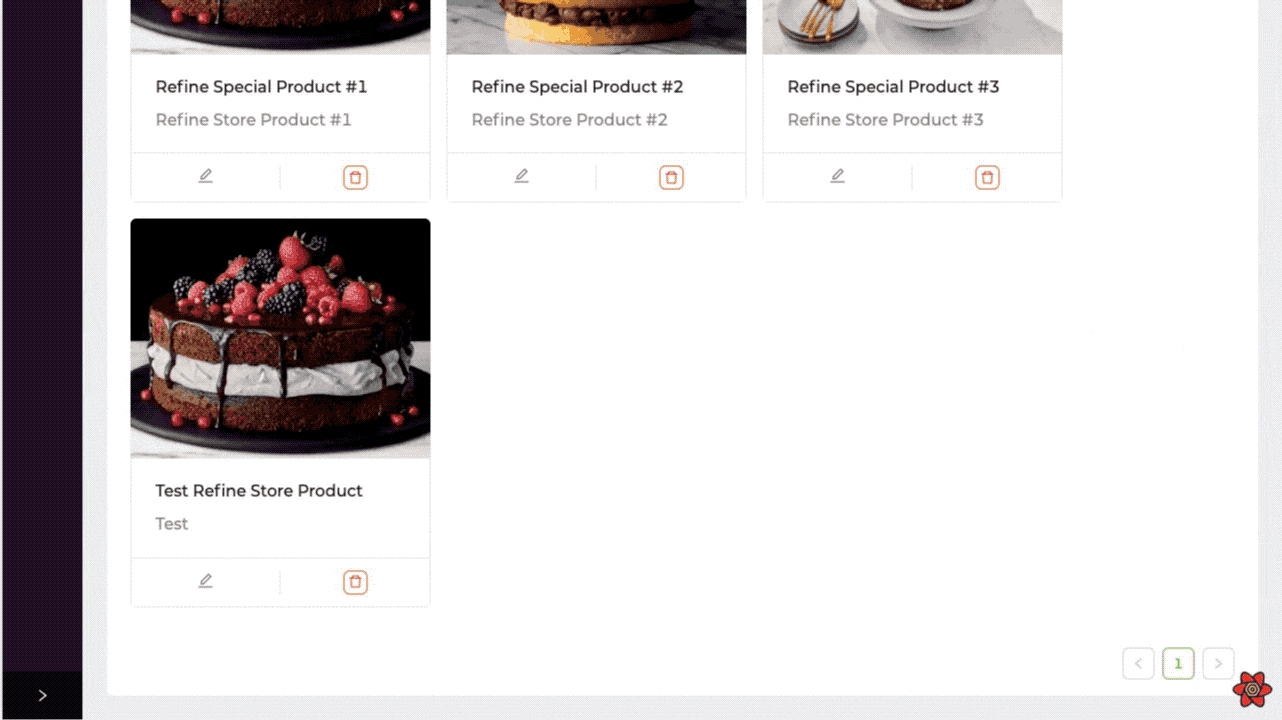
Product Create Page
Now let's see how we can create store-specific products. Which store we choose in Sider, the product we will create will automatically be the product of the selected store.
By overriding the onFinish method of the form and sending the selected store information, we specify which store it will be the product of.
const [store, setStore] = useContext(StoreContext);
<Form
{...formProps}
...
onFinish={(values) => {
return (
formProps.onFinish?.({
...values,
stores: store,
})
);
}}
>
Show Code
import { useContext } from "react";
import { useApiUrl } from "@pankod/refine-core";
import {
Create,
Drawer,
DrawerProps,
Form,
FormProps,
Input,
ButtonProps,
Upload,
Grid,
} from "@pankod/refine-antd";
import { StoreContext } from "context/store";
import {
useStrapiUpload,
mediaUploadMapper,
getValueProps,
} from "@pankod/refine-strapi-v4";
import { TOKEN_KEY } from "../../constants";
type CreateProductProps = {
drawerProps: DrawerProps;
formProps: FormProps;
saveButtonProps: ButtonProps;
};
export const CreateProduct: React.FC<CreateProductProps> = ({
drawerProps,
formProps,
saveButtonProps,
}) => {
const API_URL = useApiUrl();
const [store, setStore] = useContext(StoreContext);
const breakpoint = Grid.useBreakpoint();
const { ...uploadProps } = useStrapiUpload({
maxCount: 1,
});
return (
<Drawer
{...drawerProps}
width={breakpoint.sm ? "500px" : "100%"}
bodyStyle={{ padding: 0 }}
>
<Create saveButtonProps={saveButtonProps}>
<Form
{...formProps}
layout="vertical"
initialValues={{
isActive: true,
}}
onFinish={(values) => {
return formProps.onFinish?.({
...mediaUploadMapper(values),
stores: store,
});
}}
>
<Form.Item
label="Title"
name="title"
rules={[
{
required: true,
},
]}
>
<Input />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item label="Description" name="description">
<Input />
</Form.Item>
<Form.Item label="Image">
<Form.Item
name="image"
valuePropName="fileList"
getValueProps={(data) =>
getValueProps(data, API_URL)
}
noStyle
rules={[
{
required: true,
},
]}
>
<Upload.Dragger
name="files"
action={`${API_URL}/upload`}
headers={{
Authorization: `Bearer ${localStorage.getItem(
TOKEN_KEY,
)}`,
}}
listType="picture"
multiple
{...uploadProps}
>
<p className="ant-upload-text">
Drag & drop a file in this area
</p>
</Upload.Dragger>
</Form.Item>
</Form.Item>
</Form>
</Create>
</Drawer>
);
};
Conclusion
In this guide and our example app, we talked about how we can build Multitenancy apps with refine. Developing a Multitenancy application with refine is quite simple. By creating a context and with the hooks that refine provides, you can quickly and easily produce similar applications in this logic.
Example
Username: refine-demo
Password: demodemo
npm create refine-app@latest -- --example multi-tenancy-strapi